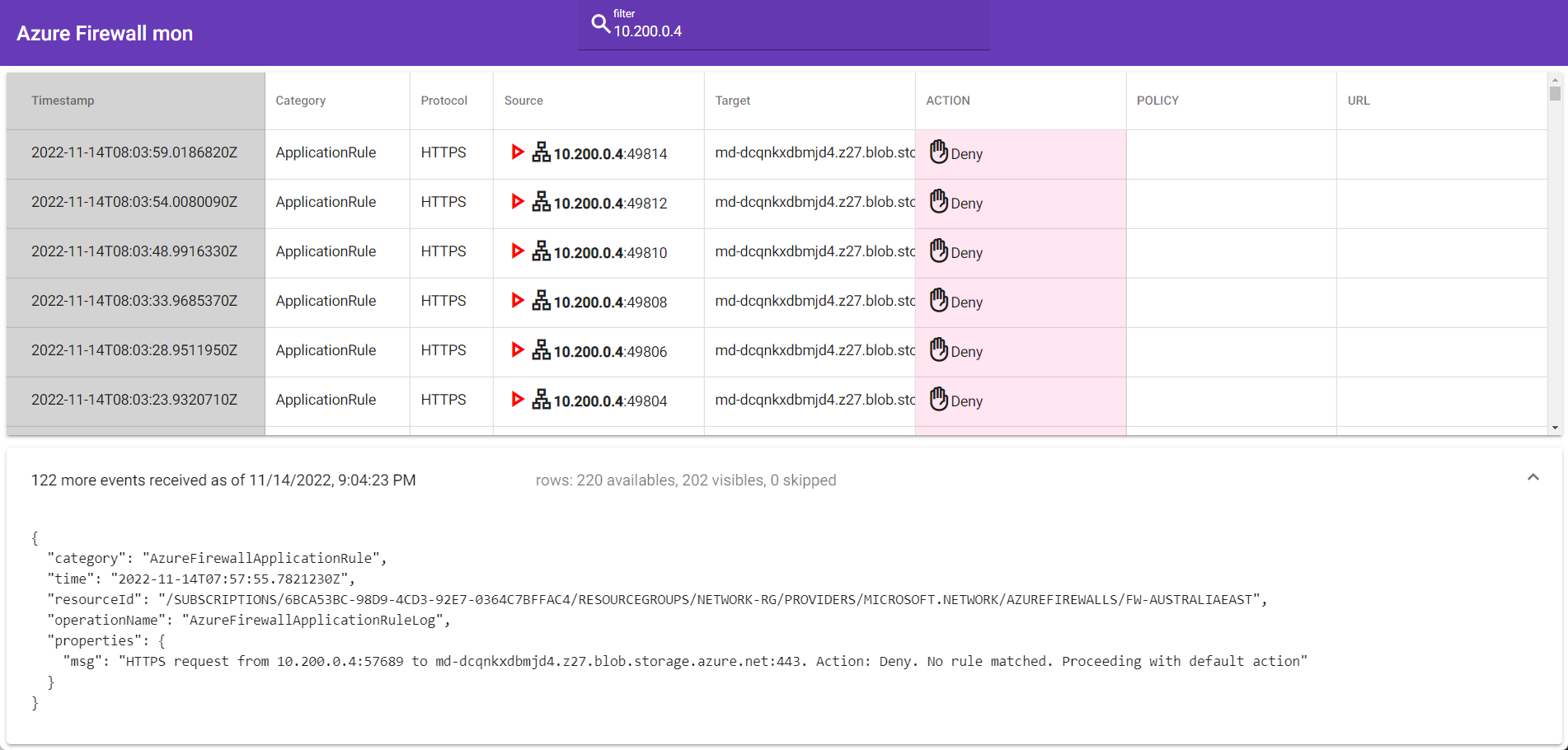
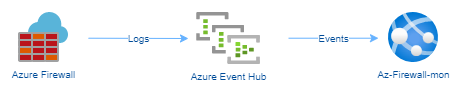
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Entra ID | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/active-directory/app-proxy/what-is-application-proxy | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Entra ID | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/active-directory/authentication/how-to-mfa-registration-campaign | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Entra ID | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/active-directory/azuread-dev/videos | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Entra ID | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/active-directory/cloud-sync/concept-how-it-works | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Entra ID | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/active-directory/develop/active-directory-claims-mapping | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Entra ID | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/active-directory/develop/custom-rbac-for-developers | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Entra ID | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/active-directory/fundamentals/secure-with-azure-ad-single-tenant | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Entra ID | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/active-directory/fundamentals/service-accounts-managed-identities | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Entra ID | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/active-directory/managed-identities-azure-resources/tutorial-linux-vm-access-cosmos-db | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Entra ID | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/active-directory/managed-identities-azure-resources/tutorial-vm-managed-identities-cosmos | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Entra ID | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/active-directory/managed-identities-azure-resources/tutorial-windows-vm-access-cosmos-db | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure DDOS Protection | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/manage-ddos-protection-powershell-ip | DDoS IP Protection PowerShell quickstart article | |
| Infrastructure | Azure DDOS Protection | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/manage-ddos-protection-cli-ip | DDoS Protection: DDoS IP Protection quickstart CLI article | |
| Infrastructure | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/types-of-attacks | DDoS Protection: Types of DDoS attacks overview | |
| Infrastructure | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/telemetry | DDoS Protection: Tutorial: View and configure DDoS protection telemetry | |
| Infrastructure | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/alerts | DDoS Protection: View and configure DDoS protection alerts | |
| Infrastructure | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/fundamental-best-practices | DDoS Protection: Fundamental best practices | |
| Infrastructure | Azure DDOS Protection | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/ddos-protection-sku-comparison | DDoS Protection: SKU comparison | Creating new document to identify differences between the SKUs. |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/alerts | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/ddos-disaster-recovery-guidance | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/ddos-faq | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/ddos-protection-overview | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/ddos-protection-partner-onboarding | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/ddos-protection-reference-architectures | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure DDOS Protection | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/ddos-protection-sku-comparison | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/ddos-rapid-response | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/ddos-response-strategy | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/diagnostic-logging | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/fundamental-best-practices | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/index | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/inline-protection-glb | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/manage-ddos-protection-bicep | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/manage-ddos-protection-cli | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure DDOS Protection | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/manage-ddos-protection-powershell-ip | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/manage-ddos-protection-powershell | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/manage-ddos-protection-template | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/manage-ddos-protection | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/manage-permissions | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/policy-reference | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/telemetry | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/test-through-simulations | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure DDOS Protection | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/ddos-protection/types-of-attacks | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure DNS | Updated | Docs | https://review.docs.microsoft.com/azure/dns/dns-private-resolver-overview | Azure DNS Private Resolver updates for GA | Removing public preview mentions and warnings, updating screenshots, etc. |
| Infrastructure | Azure DNS | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.comazure/dns/private-dns-privatednszone#restrictions | Azure DNS: Update private DNS zone restrictions | Table of zone names that are not allowed. These will be blocked the end of August '22. |
| Infrastructure | Azure DNS | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/dns/private-resolver-reliability | Resiliency in Azure DNS Private Resolver | This article describes reliability support in Azure DNS Private Resolver, and covers both regional resiliency with availability zones and cross-region resiliency with disaster recovery. |
| Infrastructure | Azure DNS | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/dns/dns-private-resolver-get-started-portal | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure DNS | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/dns/dns-private-resolver-get-started-powershell | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure DNS | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/dns/dns-private-resolver-overview | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure DNS | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/dns/private-resolver-endpoints-rulesets | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure DNS | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/dns/private-resolver-hybrid-dns | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure DNS | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/dns/tutorial-dns-private-resolver-failover | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure ExpressRoute | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/expressroute/expressroute-locations-providers | Azure ExpressRoute: Hybrid ExpressRoute (ExpressRoute Metro) | Documenting availability of locations that will soon have ExpressRoute Metro support. |
| Infrastructure | Azure Kubernetes Service | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/aks/vertical-pod-autoscaler | Vertical Pod Scaler add-on for Azure Kubernetes Service | New documentation supporting this addon's support by our service |
| Infrastructure | Azure Kubernetes Service | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/aks/cluster-configuration | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Kubernetes Service | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/aks/index | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Kubernetes Service | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/aks/intro-kubernetes | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Kubernetes Service | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/aks/monitor-aks-reference | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Kubernetes Service | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/aks/monitor-aks | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Kubernetes Service | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/aks/openfaas | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Kubernetes Service | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/aks/operator-best-practices-identity | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Kubernetes Service | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/aks/quickstart-dapr | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Kubernetes Service | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/aks/use-cvm | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Kubernetes Service | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/aks/use-mariner | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Kubernetes Service | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/aks/use-multiple-node-pools | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/app/java-standalone-profiler | Java Illuminate - Profiling via Java Flight Recorder (JFR) | The Application Insights Java profiler uses the JFR profiler provided by the JVM to record profiling data. So that users may download the JFR recordings at a later time and analyze them to identify the cause of performance issues. |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/alerts/alerts-create-new-alert-rule | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/alerts/alerts-types | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/alerts/alerts-understand-migration | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/alerts/prometheus-alerts | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/app/java-in-process-agent | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/autoscale/autoscale-understanding-settings | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/best-practices-cost | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/change/change-analysis | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/containers/container-insights-cost | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/containers/container-insights-custom-metrics | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/containers/container-insights-enable-arc-enabled-clusters | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/containers/container-insights-gpu-monitoring | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/containers/container-insights-log-query | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/containers/container-insights-metric-alerts | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/containers/container-insights-onboard | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/containers/container-insights-overview | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/containers/container-insights-prometheus-metrics-addon | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/containers/container-insights-prometheus-monitoring-addon | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/containers/container-insights-prometheus | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/data-platform | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/essentials/activity-log | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/essentials/azure-monitor-workspace-overview | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/essentials/data-collection-rule-edit | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/essentials/data-platform-metrics | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/essentials/metrics-supported | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/essentials/prometheus-metrics-multiple-workspaces | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/essentials/prometheus-metrics-overview | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/essentials/prometheus-metrics-scrape-configuration-minimal | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/essentials/prometheus-metrics-scrape-configuration | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/essentials/prometheus-metrics-scrape-default | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/essentials/prometheus-metrics-scrape-scale | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/essentials/prometheus-metrics-scrape-validate | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/essentials/prometheus-metrics-troubleshoot | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/essentials/prometheus-rule-groups | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/essentials/resource-logs | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/faq | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/index | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/logs/create-pipeline-datacollector-api | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/monitor-reference | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/observability-data | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/overview | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/resource-manager-samples | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/service-limits | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Monitor | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/azure-monitor/whats-new | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure Purview | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/purview/create-sensitivity-label | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure Purview | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/purview/how-to-automatically-label-your-content | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure Purview | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/purview/microsoft-purview-connector-overview | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure Purview | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/purview/register-scan-azure-cosmos-database | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure Security | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/security/develop/threat-modeling-tool-authorization | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure Security | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/security/develop/threat-modeling-tool-input-validation | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure Security | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/security/develop/threat-modeling-tool-sensitive-data | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure Security | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/security/fundamentals/encryption-overview | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure Security | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/security/fundamentals/feature-availability | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure Security | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/security/fundamentals/ransomware-prepare | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure Sentinel | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/sentinel/create-codeless-connector | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Azure Sentinel | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/sentinel/customer-managed-keys | | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Storage | Updated | Training | https://learn.microsoft.com/training/modules/choose-the-right-disk-storage-for-vm-workload | Refresh: Choose the right disk storage for your virtual machine workload | Need to include updates for the Premium SSD v2 to the list of disk options.
One of those offerings (premium v2) has will GA in the coming few months (date TBD)
Perhaps add a question to the Knowledge Check for the new disk type. |
| Infrastructure | Azure Virtual Network Manager | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/virtual-network-manager/concept-cross-tenant | Cross-Tenant Support Concept | |
| Infrastructure | Azure Virtual Network Manager | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/virtual-network-manager/how-to-configure-cross-tenant-portal | Cross Tenant HowTo - Portal | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/apply-security-baseline | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/attack-path-reference | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/auto-deploy-azure-monitoring-agent | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/auto-deploy-vulnerability-assessment | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/azure-devops-extension | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/concept-agentless-data-collection | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/concept-attack-path | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/concept-cloud-security-posture-management | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/concept-defender-for-cosmos | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/concept-easm | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/concept-regulatory-compliance | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/custom-dashboards-azure-workbooks | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/custom-security-policies | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/defender-for-cloud-introduction | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/defender-for-container-registries-introduction | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/defender-for-containers-architecture | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/defender-for-containers-enable | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/defender-for-containers-introduction | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/defender-for-containers-va-ecr | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/defender-for-databases-enable-cosmos-protections | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/defender-for-devops-introduction | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/defender-for-servers-introduction | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/defender-for-sql-usage | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/deploy-vulnerability-assessment-byol-vm | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/deploy-vulnerability-assessment-tvm | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/deploy-vulnerability-assessment-vm | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/detect-credential-leaks | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/enable-enhanced-security | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/enable-vulnerability-assessment-agentless | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/enhanced-security-features-overview | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/exempt-resource | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/faq-data-collection-agents | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/faq-general | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/faq-vms | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/github-action | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/how-to-manage-attack-path | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/how-to-manage-cloud-security-explorer | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/iac-vulnerabilities | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/index | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/information-protection | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/kubernetes-workload-protections | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/monitoring-components | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/os-coverage | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/overview-page | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/partner-integration | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/permissions | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/plan-multicloud-security-automate-connector-deployment | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/plan-multicloud-security-define-adoption-strategy | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/plan-multicloud-security-determine-access-control-requirements | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/plan-multicloud-security-determine-business-needs | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/plan-multicloud-security-determine-compliance-requirements | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/plan-multicloud-security-determine-data-residency-requirements | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/plan-multicloud-security-determine-multicloud-dependencies | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/plan-multicloud-security-determine-ownership-requirements | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/plan-multicloud-security-get-started | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/plan-multicloud-security-other-resources | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/policy-reference | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/powershell-onboarding | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/quickstart-onboard-aws | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/quickstart-onboard-devops | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/quickstart-onboard-gcp | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/quickstart-onboard-github | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/recommendations-reference | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/regulatory-compliance-dashboard | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/release-notes-archive | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/release-notes | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/security-center-planning-and-operations-guide | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/security-policy-concept | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/supported-machines-endpoint-solutions-clouds-containers | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/supported-machines-endpoint-solutions-clouds-servers | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/troubleshooting-guide | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/tutorial-enable-pull-request-annotations | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/tutorial-security-incident | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/tutorial-security-policy | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/update-regulatory-compliance-packages | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/workflow-automation | | |
| Security, Compliance & Identity Management | Microsoft Defender for Cloud | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/defender-for-cloud/working-with-log-analytics-agent | | |
| M365 | Microsoft Teams | New | Digital Brochure | https://aka.ms/TeamsIgnite2022Guide | Your Guide to Microsoft Teams @Microsoft Ignite 2022 | Learn about resources, main messaging, and access our digital brochure with a list of all Microsoft Teams sessions |
| M365 | Microsoft Teams | Updated | Blog | https://aka.ms/teamsignite2022MTCblog | What's New In Teams Blog: Microsoft Ignite Edition
| Discover the innovations coming to Microsoft Teams at Microsoft Ignite |
| M365 | Microsoft Teams | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoftteams/operator-connect-mobile-plan | Plan for Teams Phone Mobile | Updating existing text to show Operator Connect Mobile which will rebrand to Teams Phone Mobile after 10/12 |
| M365 | Microsoft Teams | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoftteams/operator-connect-mobile-configure | Configure Teams Phone Mobile | Updating existing text to show Operator Connect Mobile which will rebrand to Teams Phone Mobile after 10/12 |
| M365 | Microsoft Teams | New | Blog | https://aka.ms/TeamsPremiumBlog | Teams Premium Announcement | New licensing for Teams announcment happening at Ignite 2022. Details in the blog and how to get updates, including public preview in December 2022 and GA in February 2023 |
| Infrastructure | Network Watcher | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/network-watcher/azure-monitor-agent-with-connection-monitor | | |
| Infrastructure | Network Watcher | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/network-watcher/connection-monitor-connected-machine-agent | | |
| Infrastructure | Network Watcher | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/network-watcher/connection-monitor-create-using-portal | | |
| Infrastructure | Network Watcher | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/network-watcher/connection-monitor-install-azure-monitor-agent | | |
| Infrastructure | Network Watcher | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/network-watcher/frequently-asked-questions | | |
| Infrastructure | Network Watcher | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/network-watcher/index | | |
| Infrastructure | Network Watcher | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/network-watcher/network-insights-overview | | |
| Infrastructure | Network Watcher | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/network-watcher/network-insights-topology | | |
| Infrastructure | Network Watcher | New | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/network-watcher/network-insights-troubleshooting | | |
| Infrastructure | Network Watcher | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/network-watcher/network-watcher-connectivity-overview | | |
| Infrastructure | Network Watcher | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/network-watcher/network-watcher-connectivity-portal | | |
| Infrastructure | Network Watcher | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/network-watcher/network-watcher-monitoring-overview | | |
| Infrastructure | Network Watcher | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/network-watcher/view-network-topology | | |
| Infrastructure | Virtual Machines | Updated | Docs | https://learn.microsoft.com/azure/virtual-machines/disks-metrics | Disks metrics - new VM burst metrics | |