Accessing KeyVault from Azure DevOps
If you are running a Microsoft-hosted Azure DevOps agent, you may need to access a KeyVault to retrieve secrets. This is a common scenario when deploying resources to Azure.
In this post, I will show you how to access a KeyVault from an Azure DevOps pipeline by adding the IP of the Azure DevOps agent directly into your Azure Keyvault and removing it after it retrieves the secrets.

When attempting to retrieve secrets from a KeyVault using Azure DevOps, you may get an error such as:
##[error]Get secrets failed. Error: Client address is not authorized and caller is not a trusted service.
This is due to the Firewall of the Keyvault being enabled, which is best practice.
You have a few options here:
- Option 1: Enable private endpoint for the KeyVault and use a self-hosted agent. This is the most secure option, but it requires more setup and configuration, and a self-hosted agent, running on a Virtual Machine or Container Apps.
- Option 2: Add the IP of the Azure DevOps agent to the KeyVault firewall rules. This is the easiest option, but it's not the most secure, as the IP address of the Microsoft hosted agents can change (the Microsoft hosted agents have a dynamic IP address).
Not all organisations have the resources to support a self-hosted agent, so we will look at Option 2.
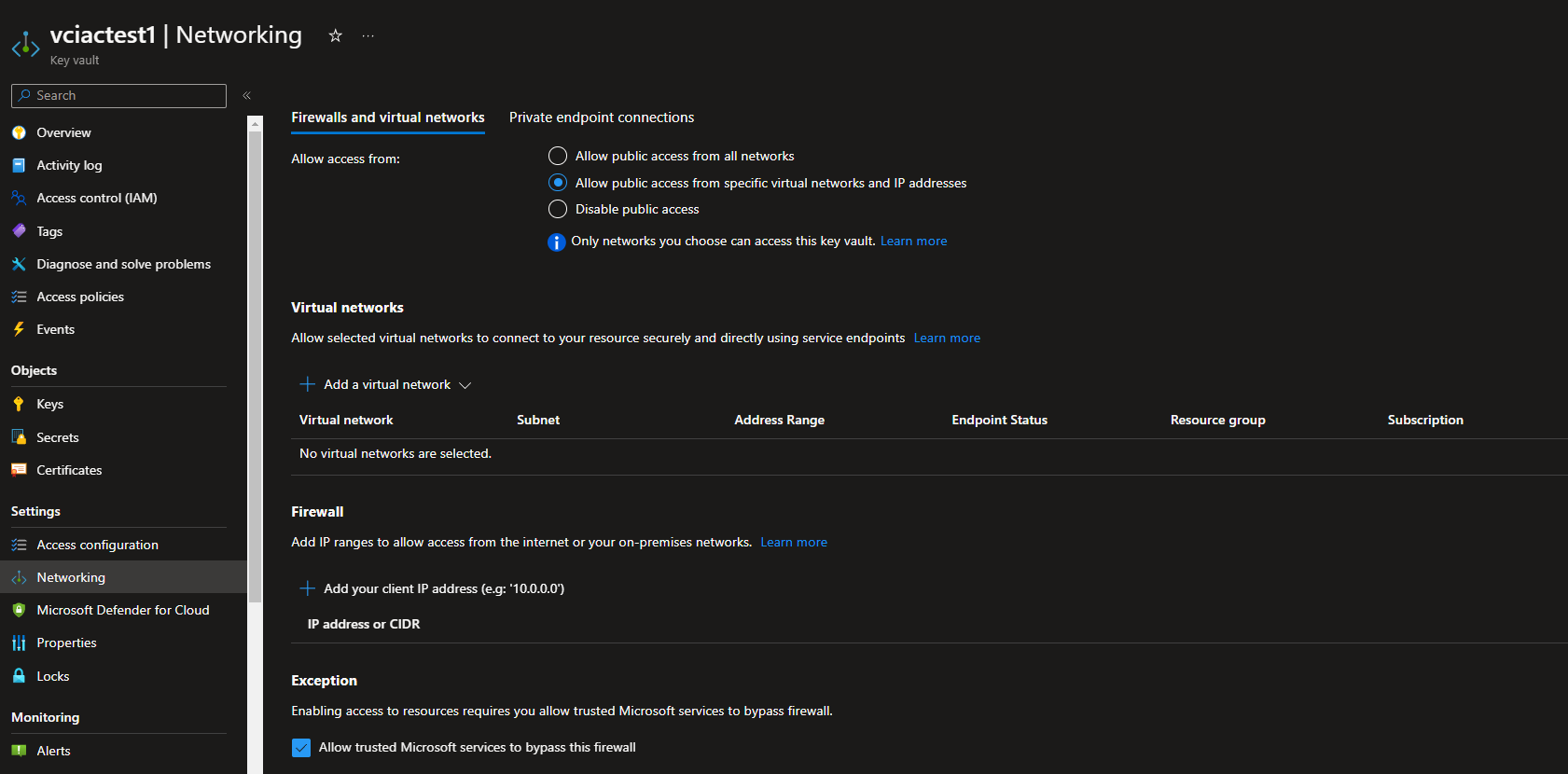
As a status, the Microsoft Hosted agents can come from any number of Microsoft-owned IP addresses from the region, that your Azure DevOps organisation is hosted.
You may immediately want to check the Allow trusted Microsoft services to bypass this firewall as an instant thought, but Azure DevOps is not an assumed trusted Microsoft service, and its not hosted within your subscription boundary.
So, that leaves us with enabling public access to the key vault, right? Because the IP will be different each time? Not quite! What we can do is:
- Add the IP of the Azure DevOps agent to the KeyVault firewall rules.
- Do the task, required from Azure DevOps (i.e. retrieve the secrets)
- Remove the IP of the Azure DevOps agent from the KeyVault firewall rules.
So, let's take a look at the Tasks you can use in your Azure DevOps pipelines to achieve this.
The following tasks use an Azure CLI command to grab the IP address of the Azure DevOps agent and then add it to the KeyVault firewall rules, and then remove it after the secrets have been retrieved, tasks below. References to the KeyVaultArmSvcConnectionName is the Service Connection that is used to authenticate to the Azure Subscription, so make sure this is adjusted for your environment. The keyVaultName is the name of the keyVault you want to access.
Note: The condition criteria is set to succeed or fail so that the task will run regardless of whether previous tasks have succeeded or failed.
# This task uses Azure CLI to add the IP address of the Azure DevOps agent to the firewall of an Azure Key Vault.
- task: AzureCLI@2 # Specifies the task to use Azure CLI version 2.
displayName: Add Agent IP From Key Vault # The name displayed for this task in the Azure DevOps pipeline.
condition: succeededOrFailed() # This task will run regardless of whether previous tasks have succeeded or failed.
inputs: # The section where you specify input parameters for the task.
azureSubscription: ${{ parameters.keyVaultArmSvcConnectionName }} # The Azure subscription that the task should use. The value is taken from the keyVaultArmSvcConnectionName parameter.
scriptType: bash # Specifies that the script to be run is a Bash script.
scriptLocation: inlineScript # Specifies that the script will be provided directly in the pipeline file, rather than being located in an external file.
inlineScript: | # Begins the section where the actual script is provided. The | character indicates that a multi-line string will follow.
agentIP=$(curl -s https://checkip.amazonaws.com) # Uses the curl command to get the public IP address of the Azure DevOps agent and stores it in the agentIP variable.
echo "Agent IP: $agentIP" # Prints the IP address to the console.
az keyvault network-rule add --name "${{ parameters.keyVaultName }}" --ip-address "$agentIP" --only-show-errors # Uses the Azure CLI to add the IP address of the Azure DevOps agent to the firewall of the Azure Key Vault specified by the keyVaultName parameter. The --only-show-errors option means that the command will only output information if an error occurs.
Remove Agent IP to KeyVault Firewall after your other tasks
# This task uses Azure CLI to remove the IP address of the Azure DevOps agent from the firewall of an Azure Key Vault.
- task: AzureCLI@2 # Specifies the task to use Azure CLI version 2.
displayName: Remove Agent IP From Key Vault # The name displayed for this task in the Azure DevOps pipeline.
condition: succeededOrFailed() # This task will run regardless of whether previous tasks have succeeded or failed.
inputs: # The section where you specify input parameters for the task.
azureSubscription: ${{ parameters.keyVaultArmSvcConnectionName }} # The Azure subscription that the task should use. The value is taken from the keyVaultArmSvcConnectionName parameter.
scriptType: bash # Specifies that the script to be run is a Bash script.
scriptLocation: inlineScript # Specifies that the script will be provided directly in the pipeline file, rather than being located in an external file.
inlineScript: | # Begins the section where the actual script is provided. The | character indicates that a multi-line string will follow.
agentIP=$(curl -s https://checkip.amazonaws.com) # Uses the curl command to get the public IP address of the Azure DevOps agent and stores it in the agentIP variable.
echo "Agent IP: $agentIP" # Prints the IP address to the console.
az keyvault network-rule remove --name "${{ parameters.keyVaultName }}" --ip-address "$agentIP" --only-show-errors # Uses the Azure CLI to remove the IP address of the Azure DevOps agent from the firewall of the Azure Key Vault specified by the keyVaultName parameter. The --only-show-errors option means that the command will only output information if an error occurs.
